Microsoft’s Windows 11, like its predecessor Windows 10, includes a built-in Telemetry System that collects data on how users interact with their devices. While the official reasoning behind this collection is to improve performance, enhance user experience, and help developers refine features, many people remain uncomfortable with the constant flow of personal and behavioral information being sent back to Microsoft.
In today’s digital age, privacy and data security are two of the most pressing concerns for both individual users and organizations. When you purchase a PC or upgrade to Windows 11, you expect it to work for you — not the other way around. However, telemetry data means that your device regularly communicates with Microsoft servers, transmitting details such as which applications you use, which settings you adjust, and even which websites you visit.
Although Microsoft positions telemetry as harmless and claims it doesn’t compromise user privacy, the sheer scope of the information collected has led many people to question whether they should allow this feature to run unrestricted. The good news is that depending on the edition of Windows 11 you are running, there are ways to either limit or completely disable telemetry data collection.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding telemetry in Windows 11, why it matters, the implications of disabling it, and step-by-step methods to turn it off across different Windows editions.
Understanding Telemetry in Windows 11
Telemetry is a system Microsoft uses to collect diagnostic and feedback information. It’s designed to give the company insight into how Windows 11 is used in real-world scenarios. The data collected ranges from basic device information and error reports to more detailed logs of how specific apps are performing.
According to Microsoft, telemetry serves four main purposes:
- Improving user experience – By analyzing how users interact with features, Microsoft can identify which tools are popular and which may need redesigning.
- Troubleshooting errors – Telemetry data can help Microsoft detect crashes, system errors, or bugs, enabling faster patch releases.
- Security enhancements – Reports of security vulnerabilities or exploit attempts can help Microsoft develop protective measures.
- Product development – By studying aggregated usage patterns, Microsoft can decide where to focus future innovations.
While these intentions are reasonable from a software development perspective, users often see telemetry as intrusive. For example, system logs may reveal browsing habits, app usage, or work-related activities, which many people consider private. Even though Microsoft assures that personal identifiers are minimized, there is always a risk when sensitive information leaves your device.
Why Some Users Want to Disable Telemetry
There are several reasons why Windows 11 users actively seek to limit or turn off telemetry data collection:
- Privacy concerns – Many users do not want their activity tracked or stored by an external company. Even if the data is anonymized, the very act of data collection feels invasive.
- Regulatory compliance – Businesses handling sensitive or regulated data may not be allowed to share system usage logs with third parties, even unintentionally.
- Performance issues – Some users believe that background telemetry processes consume system resources and slow down their PCs, although Microsoft claims the impact is minimal.
- Control over data – In an era where data is often monetized, users feel more comfortable when they decide what information leaves their device.
Understanding these motivations is critical because they highlight a broader debate: convenience versus privacy. While telemetry might improve Windows over time, it does so at the expense of individual data sovereignty.
Can You Turn Off Telemetry in Windows 11?
The answer depends on which edition of Windows 11 you are running.
- Windows 11 Home – Users cannot completely disable telemetry, but they can restrict optional diagnostic data collection.
- Windows 11 Professional, Enterprise, and Education – Users can disable telemetry fully using either the Windows Registry Editor or the Group Policy Editor.
This division demonstrates Microsoft’s strategy: while advanced users and organizations are allowed more control, home users are nudged toward keeping telemetry active by default.
Limiting Telemetry in Windows 11 Home
Windows 11 Home edition users face certain limitations. Microsoft does not provide a way to completely disable telemetry on this edition, likely because most home users are less familiar with registry edits or group policy adjustments. However, you can still reduce the amount of data collected by turning off optional diagnostic data.
Here’s how:
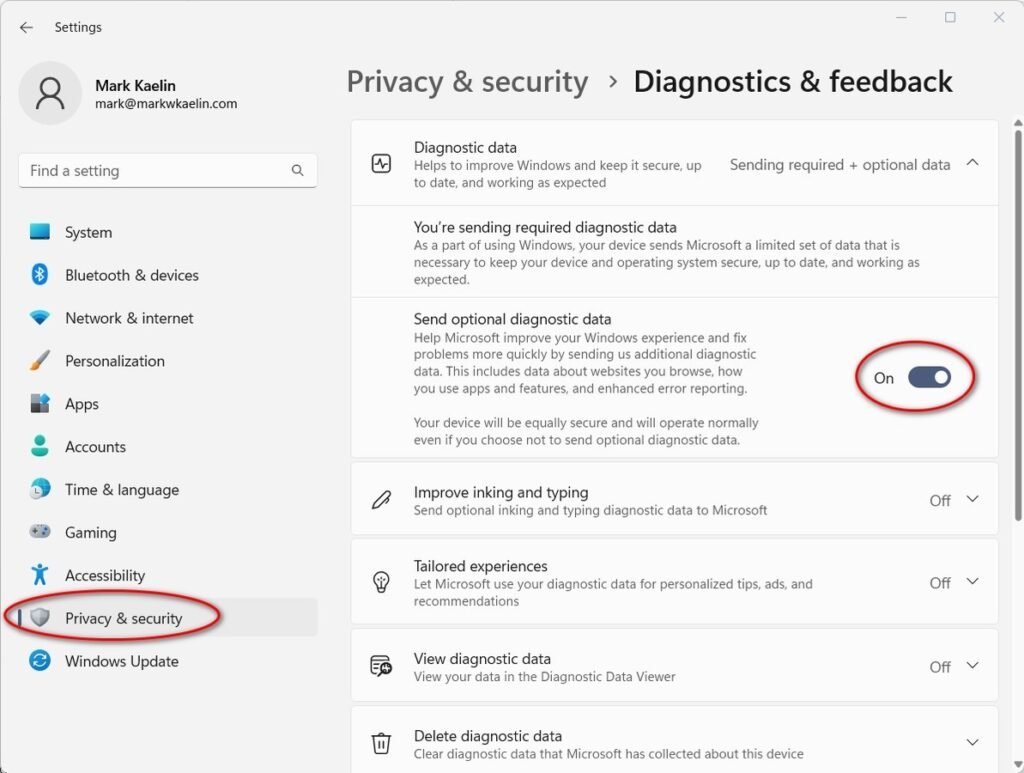
- Open the Start Menu and select the Settings app.
- In the left-hand panel, choose Privacy & Security.
- Scroll down the right-hand list until you find Diagnostics & Feedback.
- Under the diagnostics options, turn off the setting labeled Send optional diagnostic data.
This ensures that only the required minimum diagnostic information is sent to Microsoft. While you cannot eliminate telemetry entirely on Windows Home, this step significantly reduces the scope of data collection.
Disabling Telemetry in Windows 11 Professional (and Above)
If you are running Windows 11 Professional, Enterprise, Education, or Windows Server 2016 or later, you have more powerful options at your disposal. Microsoft allows advanced users and IT administrators to disable telemetry using system tools like the Registry Editor or Group Policy Editor.
Method 1: Using the Registry Editor
The Registry Editor is a powerful tool that lets you control deep system behaviors. To disable telemetry through the registry:
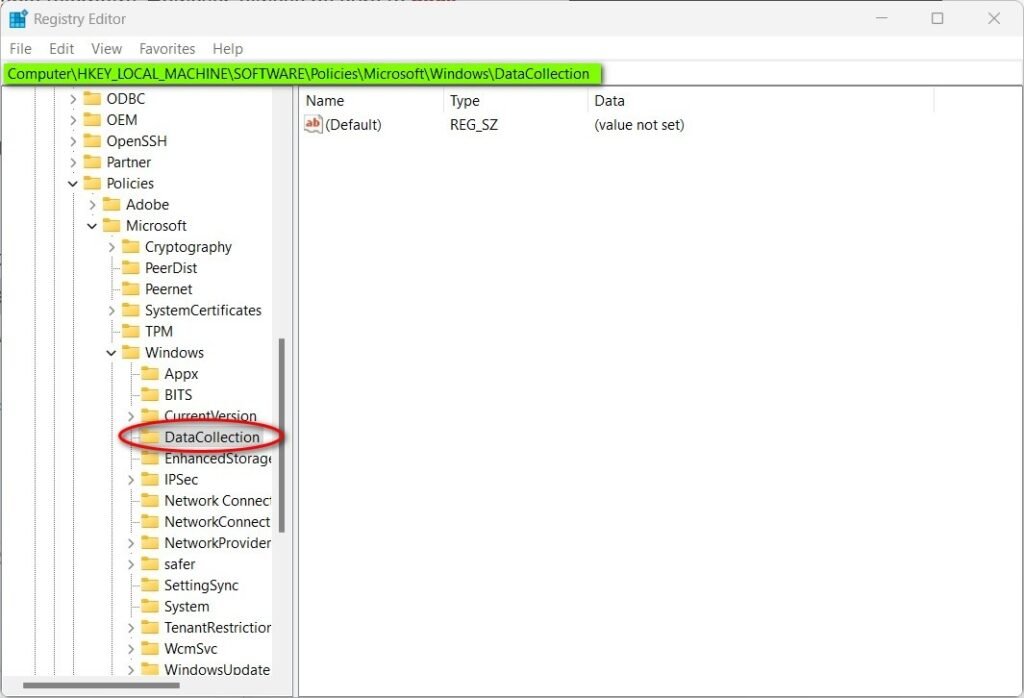
- Type regedit in the Windows search bar and open the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the following key:
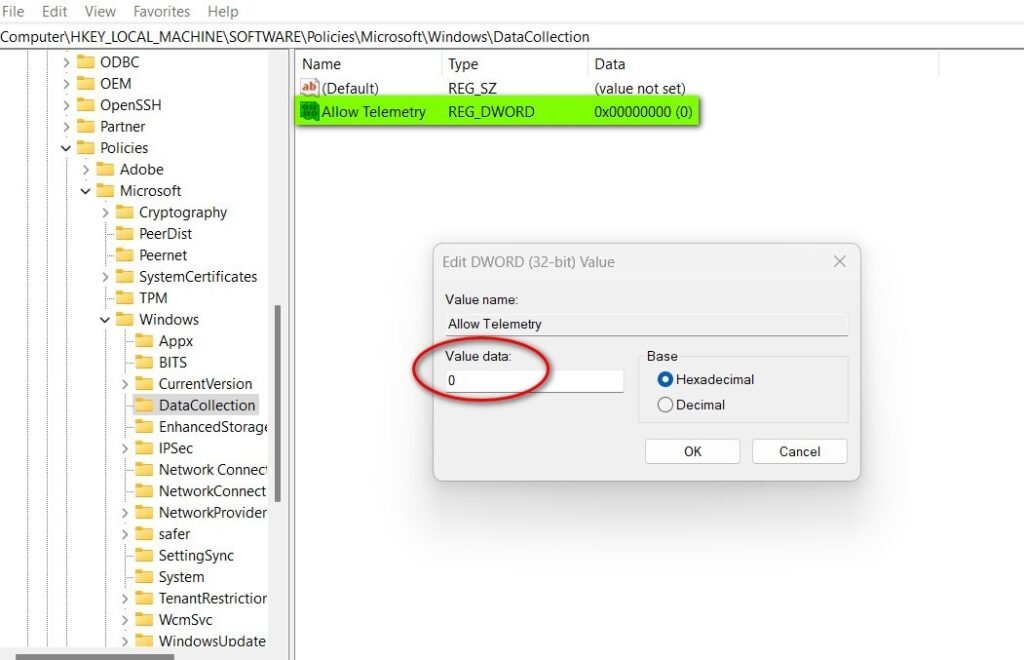
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DataCollection - Right-click on the DataCollection folder and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name the new entry Allow Telemetry.
- Double-click the entry and set its Value data to 0.
- Click OK, close the Registry Editor, and restart your PC.
This effectively blocks telemetry data collection, shielding your PC activity from Microsoft.
Method 2: Using the Group Policy Editor
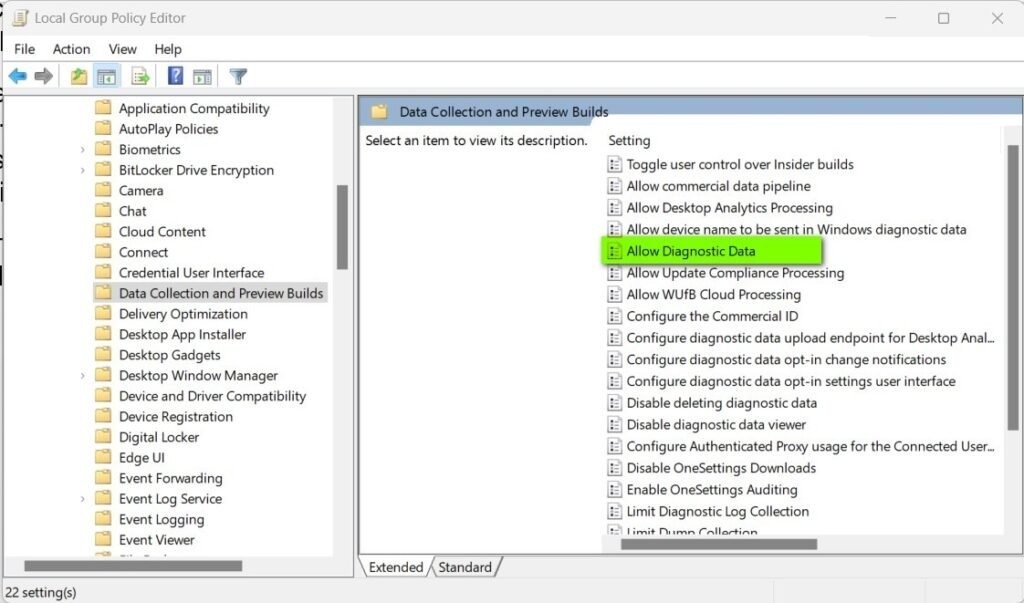
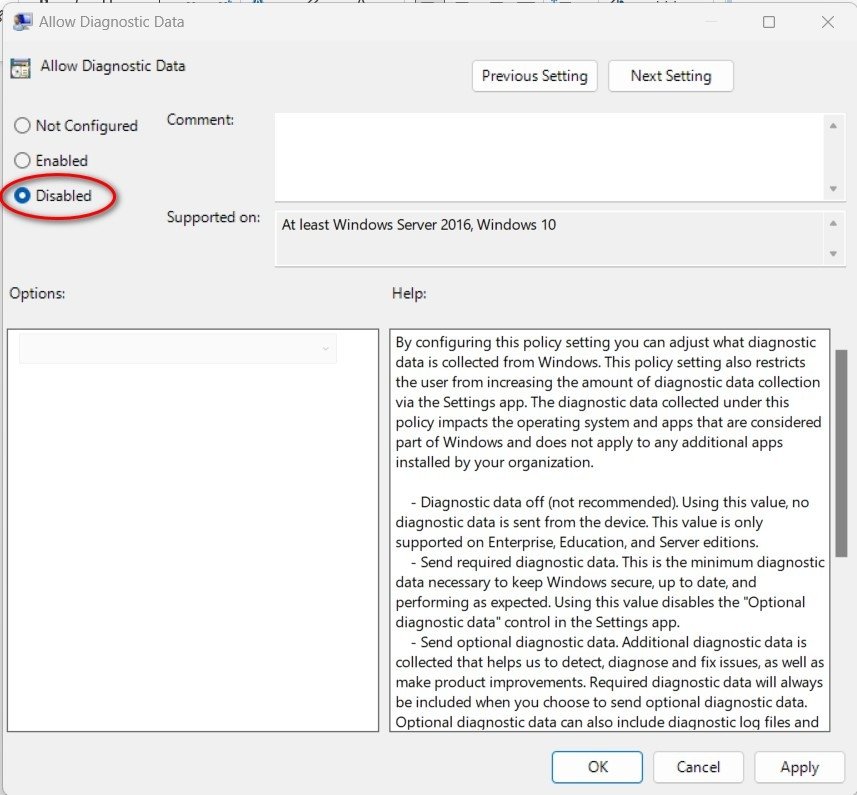
The Group Policy Editor provides a graphical interface for advanced settings management. To turn off telemetry via Group Policy:
- Type group policy in the search box and open Edit Group Policy.
- Navigate using the left panel to:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Data Collection and Preview Builds - In the right panel, locate Allow Diagnostic Data.
- Double-click it and select the Disabled radio button.
- Click OK, close the editor, and reboot your PC.
This ensures that Windows stops sending telemetry data. Unlike Windows Home, this method gives Professional and Enterprise users complete control.
Re-Enabling Telemetry (If Needed)
Sometimes, you may want to restore telemetry. For example, certain Windows Insider Preview builds or beta testing features may require diagnostic data to function properly.
To re-enable telemetry:
- Registry Editor – Change the Allow Telemetry value back to 1.
- Group Policy Editor – Set Allow Diagnostic Data to Enabled or revert it to its default setting.
This flexibility allows users to switch telemetry back on when necessary without reinstalling Windows.
The Privacy vs. Functionality Trade-Off
Before you disable telemetry entirely, it’s worth considering the consequences. While privacy improves, you may lose some benefits:
- Reduced personalized support – Microsoft uses telemetry to identify and resolve common issues. Disabling it may reduce troubleshooting accuracy.
- Limited feedback loop – Features you dislike or bugs you encounter may not reach Microsoft without manual reporting.
- Compatibility issues – Certain enterprise tools or preview builds require telemetry to function.
That said, many users find these trade-offs worthwhile, especially in environments where privacy and control take precedence over convenience.
Alternative Ways to Enhance Privacy
Disabling telemetry is only one part of a broader privacy strategy in Windows 11. Other measures include:
- Turning off targeted advertising – Found under Privacy settings.
- Disabling activity history – Prevents Microsoft from storing timeline activity.
- Managing app permissions – Restrict which apps access your location, camera, or microphone.
- Using local accounts – Avoids syncing personal data across devices via Microsoft accounts.
When combined with telemetry restrictions, these adjustments create a much more private computing environment.
The Bigger Picture: Data Collection in the Digital Age
Microsoft is not alone in collecting user data. Tech giants like Google, Apple, and Facebook also use telemetry-like systems to refine their services. However, Windows 11 stands out because it is not just an app or online service — it’s the operating system that underpins nearly all PC usage.
This means telemetry in Windows is particularly significant: it has the potential to record every digital action on a computer. The debate around this issue is part of a wider discussion about data rights, transparency, and digital independence.
Organizations like the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) have raised concerns about forced data collection, advocating for clearer user consent and greater control. Whether or not Microsoft changes its policies in future updates, users should remain proactive about protecting their privacy.
Final Thoughts
Telemetry in Windows 11 is a double-edged sword. On one hand, it provides Microsoft with the insights needed to enhance performance, patch vulnerabilities, and create better user experiences. On the other, it collects sensitive usage information that many individuals and organizations would rather keep private.
If you’re running Windows 11 Home, you can limit but not eliminate telemetry. If you’re running Windows 11 Professional, Enterprise, or Education editions, you can disable it entirely using the Registry Editor or Group Policy Editor. While there are trade-offs, the decision ultimately rests on how much value you place on privacy versus convenience.
As technology continues to evolve, the tension between user autonomy and corporate data collection will remain a central issue. Understanding your options and taking control of your settings is the best way to strike a balance that aligns with your personal values.

